Google Analytics vs Google Tag Manager: Key Differences
Benjamin Mangold
Understanding your website’s performance and how people interact with your content is key to improving your online presence. This is where tools like Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and Google Tag Manager (GTM) come into play.
While both tools are incredibly valuable, they serve different purposes. Knowing what each tool does – and when to use them – can help you make smarter, data-driven decisions for your marketing strategy.
In this guide, we’ll explore the differences between Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager, how they complement each other, and how you can use them together for even better results.
What Is Google Analytics?
Google Analytics 4 is a powerful tool that tracks and reports how users interact with your website or app. It collects data through a JavaScript tag (called the Google Tag) added to your site, giving you insights to improve content, user experience, and marketing strategies.
GA4 allows you to track important metrics like sessions (the number of visits), users (unique visitors), engagement rate (how actively people interact with your site), and conversions (completing goals like purchases or signups). You can also monitor page views and other behaviors to understand the customer journey.
By analyzing this data, you can:
- Identify your most popular pages and content
- Understand where your visitors are coming from – like organic search, social media, or referrals
- Improve your website’s user experience by finding and fixing high-exit pages
- Measure the impact of your marketing efforts with conversion tracking
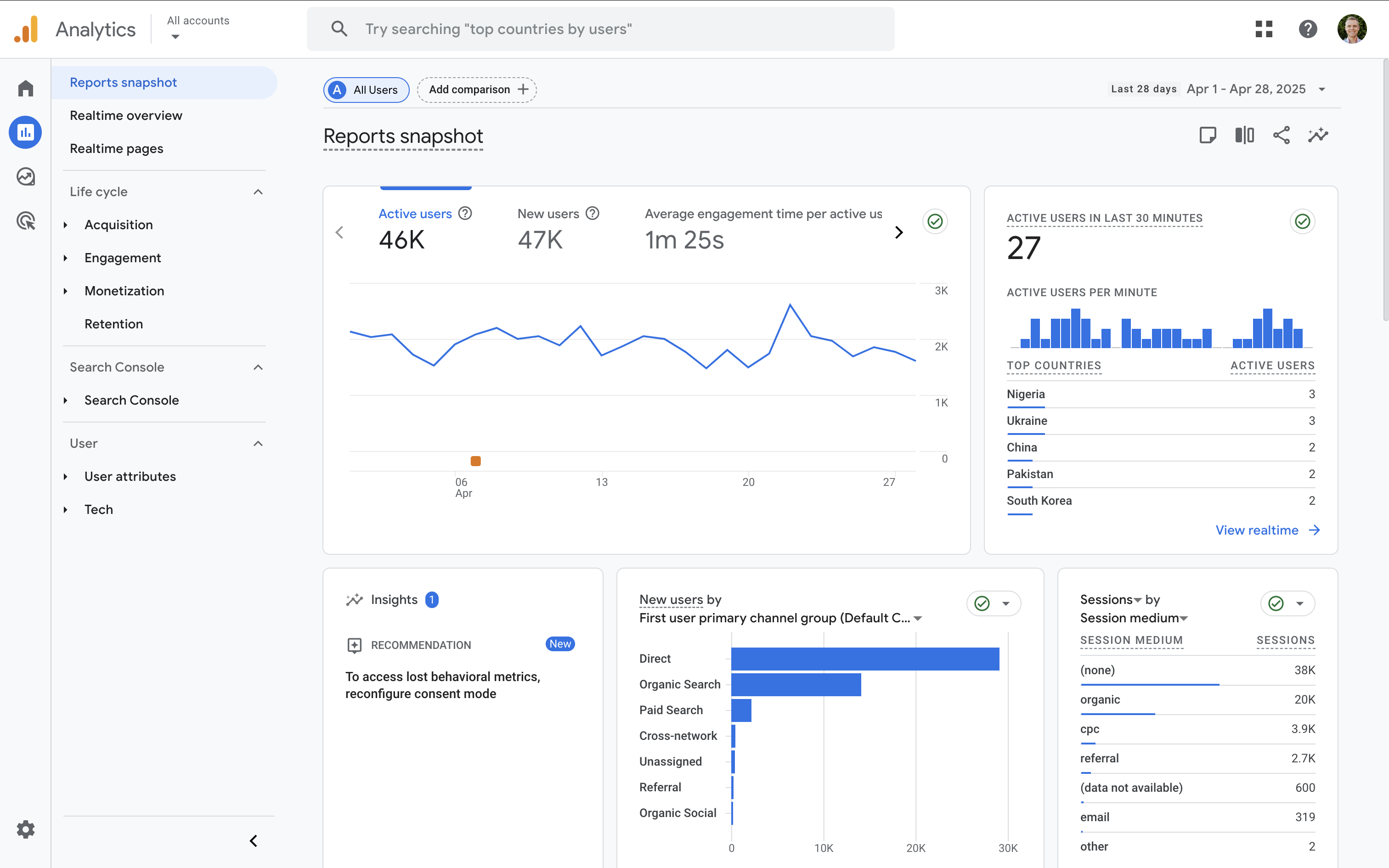
GA4 also integrates seamlessly with other Google tools like Google Ads, Google Search Console, and Looker Studio, giving you a more complete view of performance across your channels.
What Is Google Tag Manager?
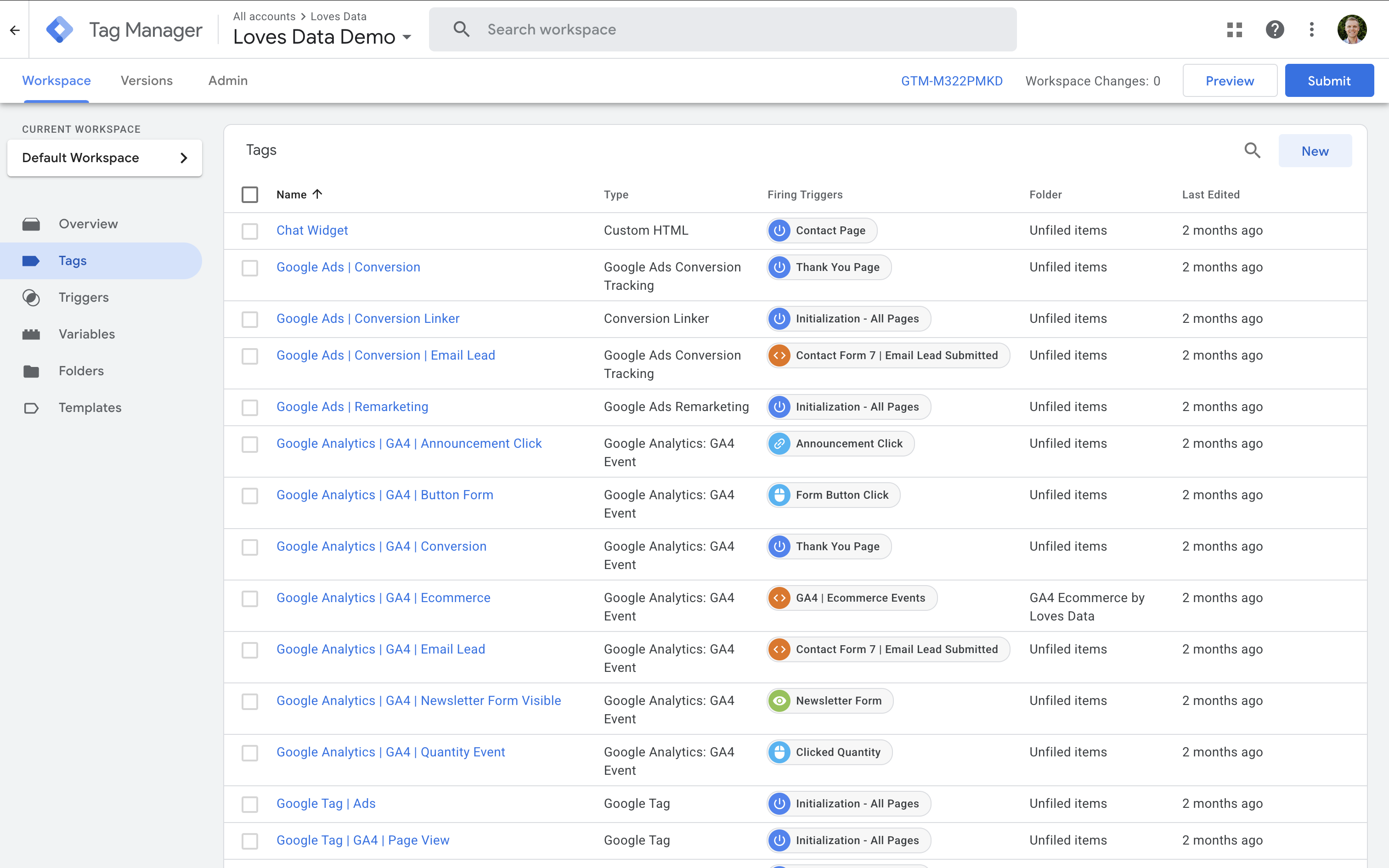
Google Tag Manager is a tag management platform that lets you easily add and update tracking codes on your website without touching the site's core code. Instead of asking developers for every small change, you can manage everything inside a simple workspace.
GTM includes features like built-in templates for popular tags (such as GA4, Google Ads, and Meta Pixel for Facebook), flexible trigger and variable options, version control, and Preview Mode to test changes before they go live.
With GTM, you can:
- Quickly deploy and update tracking codes
- Reduce reliance on developers for changes
- Use Preview Mode to test and debug your setup
- Organize all your tags in one central place
Differences Between Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager
Although they often work together, GA4 and GTM serve very different purposes. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Google Analytics 4 (GA4) | Google Tag Manager (GTM) |
|---|---|---|
| Main Purpose | Analyzes website and app user behavior | Manages deployment of tracking tags |
| Data Collection | Processes and reports user interactions | No data collection – manages tracking setup |
| Interface | Reporting and analysis dashboard | Tag and trigger management workspace |
| Key Use | Measuring performance, conversions, engagement | Deploying GA4, Google Ads, remarketing tags, and more |
| Setup | Requires adding the Google Tag (gtag.js) | Requires adding the GTM container snippet |
| Reporting | Provides detailed reports and insights | No reporting – only manages the deployment of tags |
| Ideal For | Understanding audience behavior and campaign performance | Managing multiple tracking codes without editing website code |
Beyond GA4, GTM can also manage other tags like Google Ads conversion tracking and remarketing. By setting up both GA4 and Google Ads tags inside GTM, you ensure consistent data capture across platforms – and you only need to update things in one place.
For example, you can use GTM to track form submissions or video plays as custom events, and send those events to both GA4 and Google Ads as conversions. This saves time and improves accuracy.
When to Use Each Tool
Use Google Analytics 4 when you want to measure how your website or app is performing, understand how visitors behave, and track conversions. GA4 helps you answer questions like: "How many people visited?" or "Which campaign drove the most signups?"
Use Google Tag Manager when you want to easily deploy or update tracking codes without needing to ask a developer each time. It’s especially helpful if you’re managing multiple platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and others alongside GA4.
Do You Need to Use Them Together?
In most cases, the answer is yes.
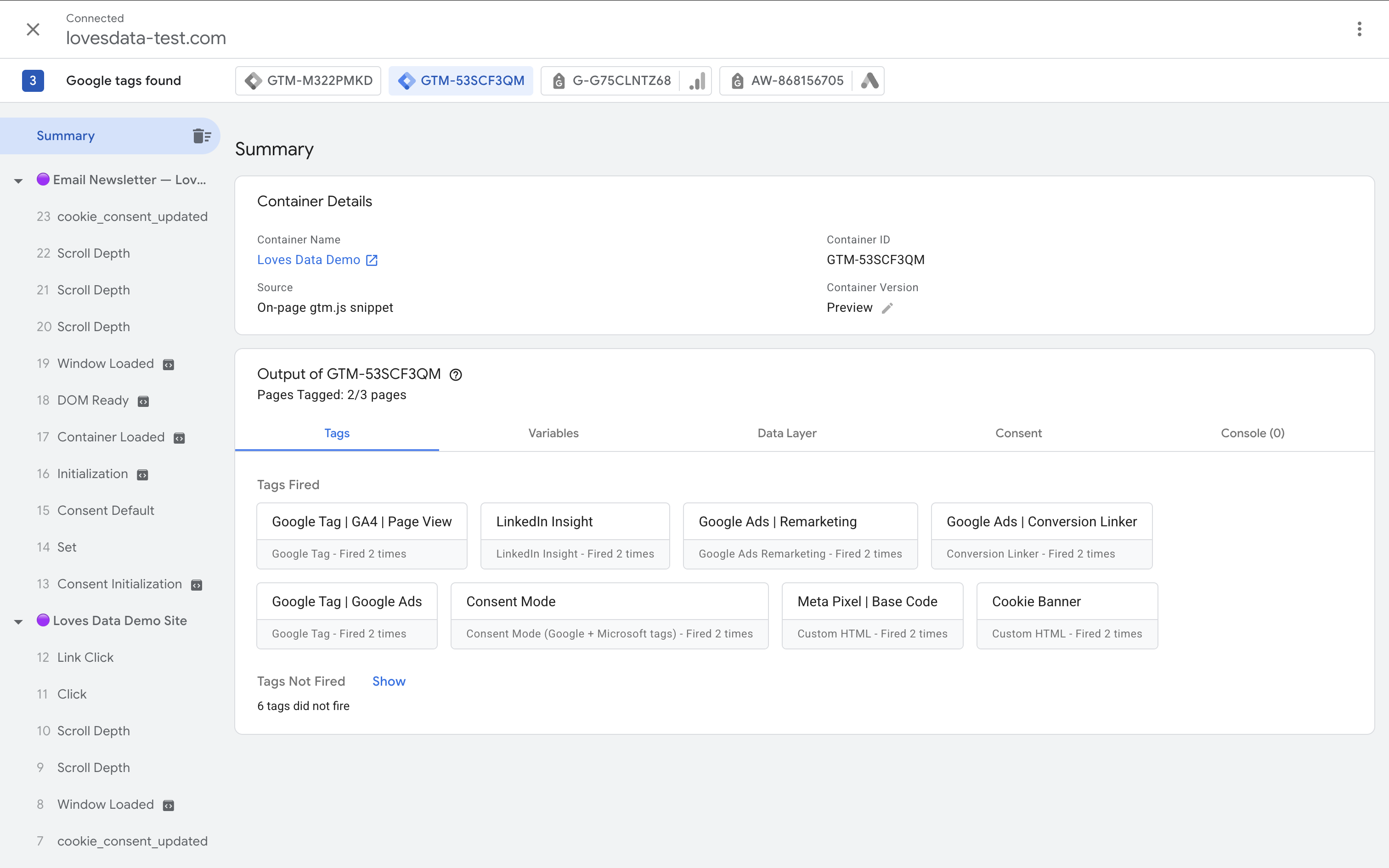
Using GTM and GA4 together streamlines your tracking setup. You can use GTM to install your GA4 configuration and event tags without editing your website code manually. GTM also makes it easy to add additional tracking, such as form submissions, outbound clicks, or video views – all without extra developer work.
Benefits of using both:
- Simplifies tag management
- Speeds up tracking updates for campaigns
- Enables custom event tracking without hardcoding
- Provides reliable, scalable reporting through GA4
Best practice tip: Always test your GTM setup using Preview Mode before publishing! It helps catch errors before your data is affected.
Conclusion
Choosing between Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager isn’t necessary – they work best together.
Google Analytics gives you the insights you need to make data-driven decisions. Google Tag Manager makes it easier to manage, deploy, and update your tracking setup without getting bogged down in code changes.
Checklist – Setting Up GTM and GA4 Together
If you’re ready to get started, here’s a quick checklist for installing Google Tag Manager and adding GA4 to your website:
- Create a Google Tag Manager account at tagmanager.google.com and set up a new container for your website.
- Install the GTM container code on your website. This means adding the container code in the
<head>tag. - Add GA4 to GTM tag by creating a new tag and selecting 'Google Tag' as the tag types, then enter your GA4 Measurement ID (from your GA4 property).
- Set the trigger to ‘Initialization - All Pages’ so your GA4 tag fires across your site.
- Use GTM’s Preview Mode to test that the GA4 tag is firing correctly before publishing.
- Publish your container when everything is working.
Tip: You can also add other tags like Google Ads or Meta Pixel inside GTM – keeping everything in one place makes tracking easier to manage.
If you’re ready to master GA4 and GTM, check out our Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager courses. You’ll learn step-by-step how to set up, track, and interpret your data – giving you the confidence to improve your marketing and website results.
